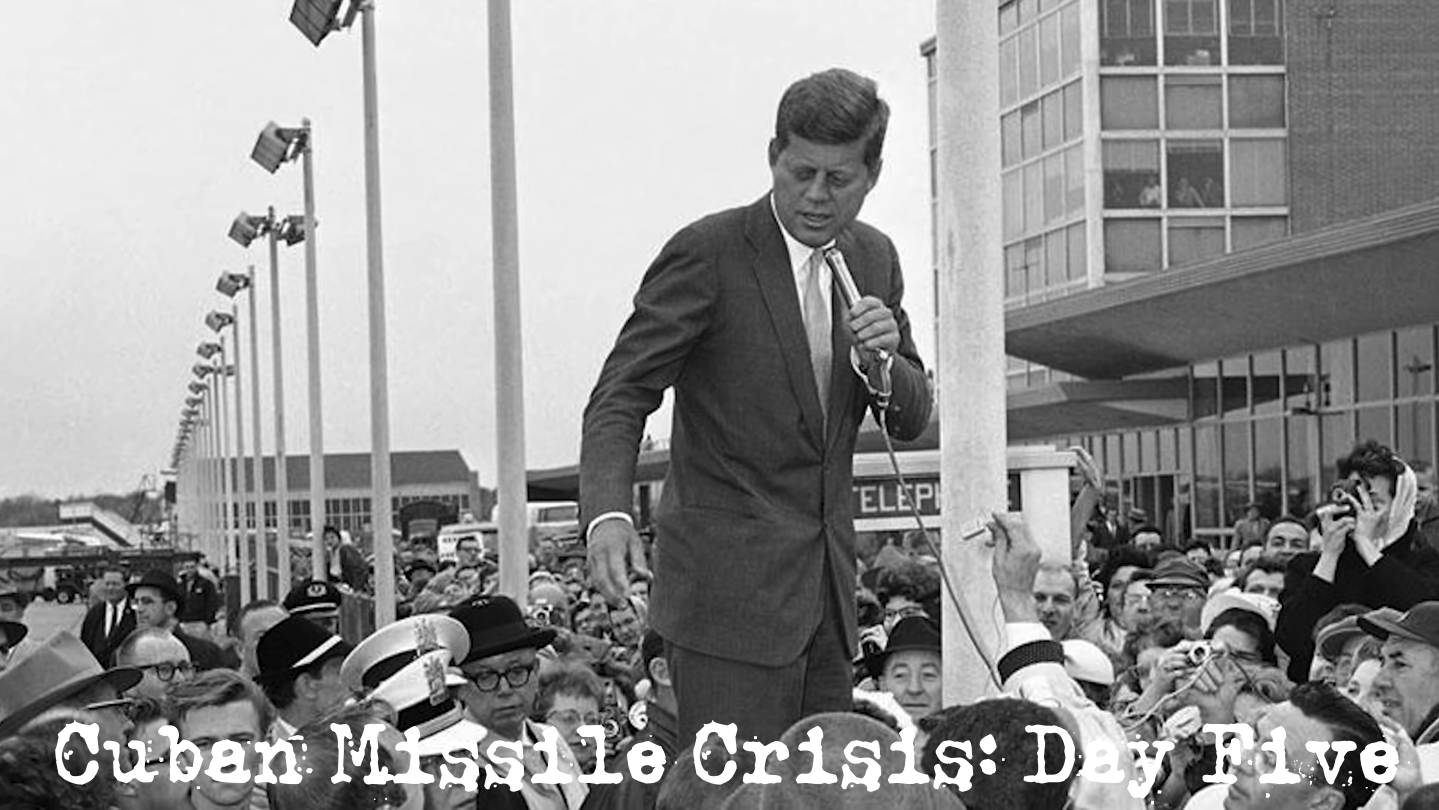Who Killed Bobby?
Who Killed Bobby? 2018 Collection: In honor of the 50th anniversary (remember I said last week that this is the year of the… Read More »Who Killed Bobby?
Who Killed Bobby? 2018 Collection: In honor of the 50th anniversary (remember I said last week that this is the year of the… Read More »Who Killed Bobby?
Cuban Missile Crisis: Day Fourteen But you didn’t see this post coming, did you? Because everyone knows that the crisis only lasted for thirteen days. After… Read More »Cuban Missile Crisis: Day Fourteen
The Cuban Missile Crisis: Day Thirteen Sunday, October 28, 1962: The thirteen days of the Cuban Missile Crisis came to an end. In… Read More »Cuban Missile Crisis: Day Thirteen
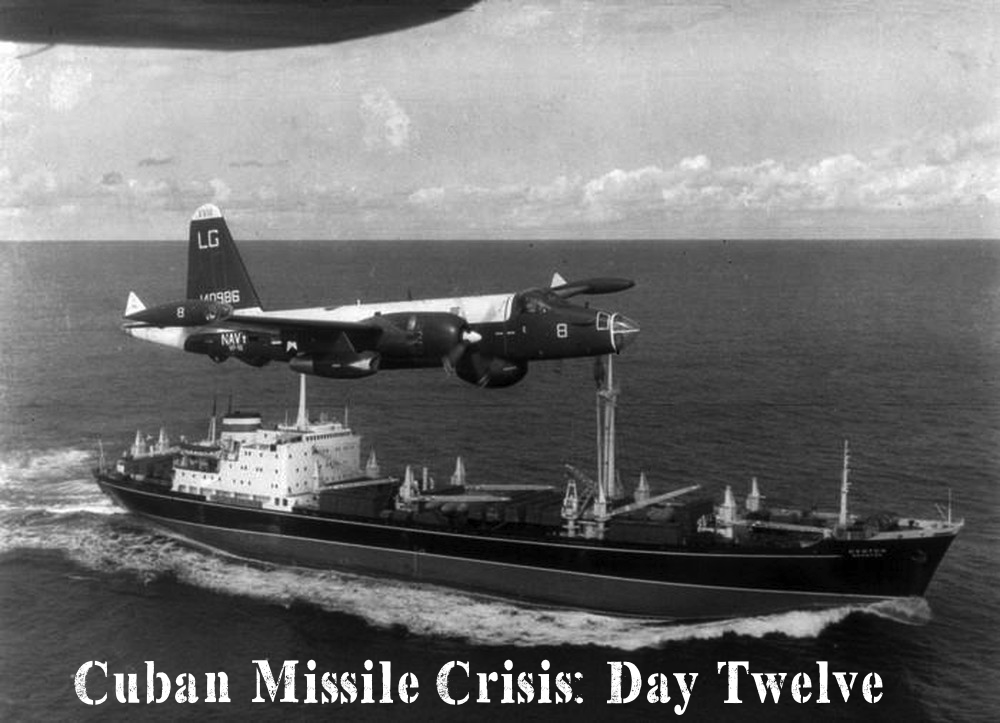
Cuban Missile Crisis: Day Twelve “Thus began the most difficult twenty-four hours of the missile crisis” (71). Saturday, October 27, 1962: A… Read More »Cuban Missile Crisis: Day Twelve
Cuban Missile Crisis: Day Eleven Friday, October 26, 1962: A Soviet-chartered freighter was stopped at the quarantine line and searched for contraband military supplies. None… Read More »Cuban Missile Crisis: Day Eleven
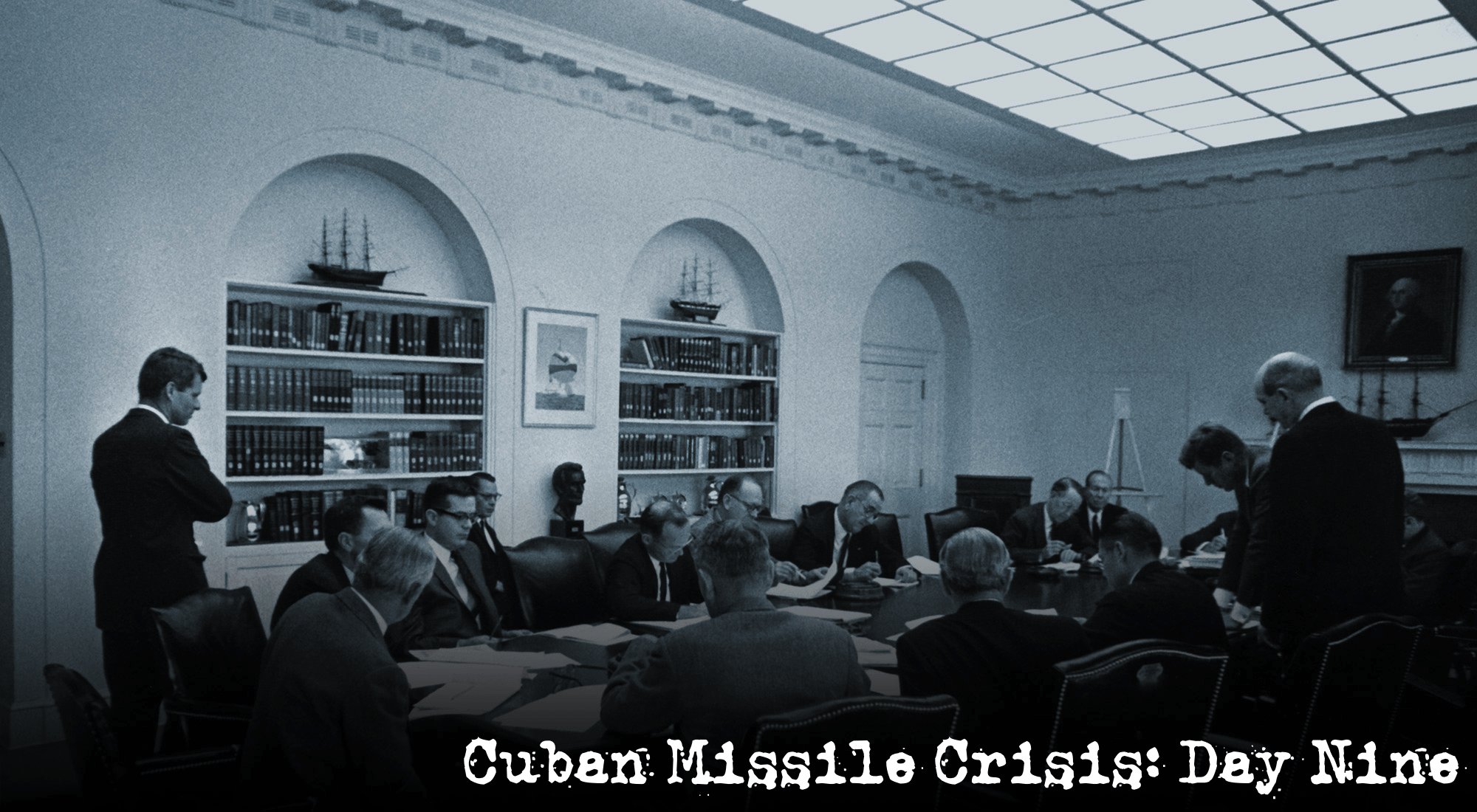
Cuban Missile Crisis: Day Nine Wednesday, October 24, 1962: The ExComm met as the quarantine went into effect. By a little after 10, they… Read More »Cuban Missile Crisis: Day Nine
Cuban Missile Crisis: Day Eight Tuesday, October 23, 1962: The ships of the naval quarantine fleet moved into place around Cuba. Soviet submarines threatened the… Read More »Cuban Missile Crisis: Day Eight
Cuban Missile Crisis: Day Five “I had heard the military take positions, which if wrong, had the advantage that no one would be around at… Read More »Cuban Missile Crisis: Day Five
Cuban Missile Crisis: Day Four Friday, October 19, 1962: President Kennedy leaves for a scheduled campaign trip to Ohio and Illinois. In Washington, his advisers… Read More »Cuban Missile Crisis: Day Four
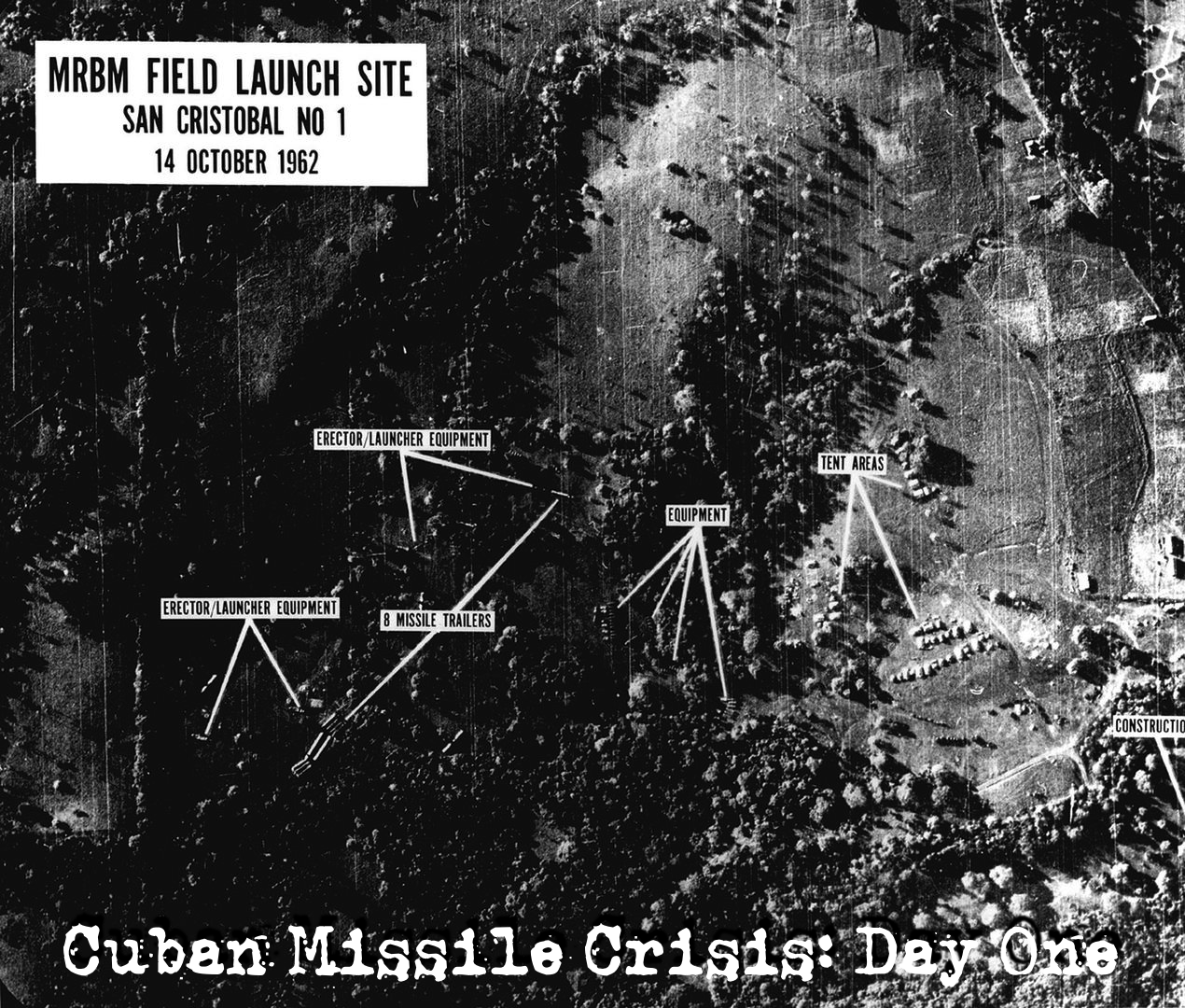
Cuban Missile Crisis: Day One At 8:45 AM on Tuesday, October 16, 1962, President Kennedy, still in his pajamas, had his breakfast interrupted by National Security… Read More »Cuban Missile Crisis: Day One